Intelligence Hub
Economic Briefing October 2024
Summary
In response to reader feedback, as well as providing a summary of the macroeconomic trend, briefings will now feature an in-depth review on specific topics of interest. These will be designed to provide greater insight on the latest research around the topic.
This month’s focus is on Regional Skills
Skills development is a cornerstone of Glasgow City Region’s (GCR) economy, vital for sustaining growth across sectors. The Region’s higher and further education institutions play a significant role in equipping the workforce with necessary skills, particularly in STEM fields like Computing, Engineering, and Veterinary Sciences, where GCR shows strong specialisations.
Despite these strengths, GCR faces challenges in aligning workforce skills with industry needs. Skill shortages, particularly in technical and vocational areas, remain a significant barrier to business expansion and economic growth. The Region must focus on improving educational outcomes and vocational training to bridge this gap, especially in sectors like Advanced Manufacturing and Precision Engineering, which are increasingly reliant on specialised technical skills.
While the Region faces challenges like economic disparities and skills gaps, it has strong foundations in a diverse range of sectors. By aligning skills with industry needs GCR can use targeted policies like the Future Skills Programme and Innovation Action Plan to build a resilient and innovative workforce.
Economic Overview
The UK’s economic outlook for mid-2024 is mixed. GDP growth has remained sluggish, but inflation has fallen to 1.7%.
The UK’s economic outlook, while cautiously optimistic, faces several challenges.
Growth: Sluggish growth in GDP also reflects broader challenges and continued issues within the labour market. Economic stagnation is posing significant challenges for public finances and fiscal sustainability, especially in the context of rising public debt and the need for investment in critical areas like infrastructure, digital transformation, and green technologies. The Autumn Statement has been set out to outline plans to ensure that new and current spending will be offset by savings elsewhere, or by measures to boost tax revenues. This could involve reforms to tax policy, such as tightening loopholes, adjusting rates, expanding the tax base, to create a higher revenue stream – or even changing the definition of public debt.
Labour Market: The latest labour market data for Scotland, covering the period from June to August 2024, shows a slightly improved picture compared to the poor figures observed in recent months. Employment in Scotland edged up to 73.7%, while unemployment has decreased to 3.9%, down 0.9 of a percentage point compared to the previous period (May – July 2024)
The primary challenges continue to centre on improving employment support, enhancing skills, and addressing health issues, with Scottish Economic Inactivity increasing by around 40,000 over the year. Further headline data is provided at the end of this document.
GCR's Economy
Cluster Overview
Glasgow City Region’s clusters in Energy & Net Zero, Advanced Manufacturing, and Digital Industries combine existing strengths with emerging specialisms.
Glasgow City Region has emerging and existing strengths in the Innovation Economy.
Supporting and investing in new sectors that promise high growth, sustainability, and adaptability will ensure that the Region can combat future economic challenges and uncertainties effectively. By fostering a diverse economic base that leverages both traditional strengths and emerging opportunities, Glasgow City Region will be better equipped for the future.
- But to support the innovation economy, the Region must have a steady pipeline of talent to support the growth in future sectors, particularly around the Green Economy.
- Evidence suggests that skills gaps exist in the innovation economy, limiting growth of the Region’s key sectors and clusters.
Figure 1: GCR’s Emerging and Existing Strengths
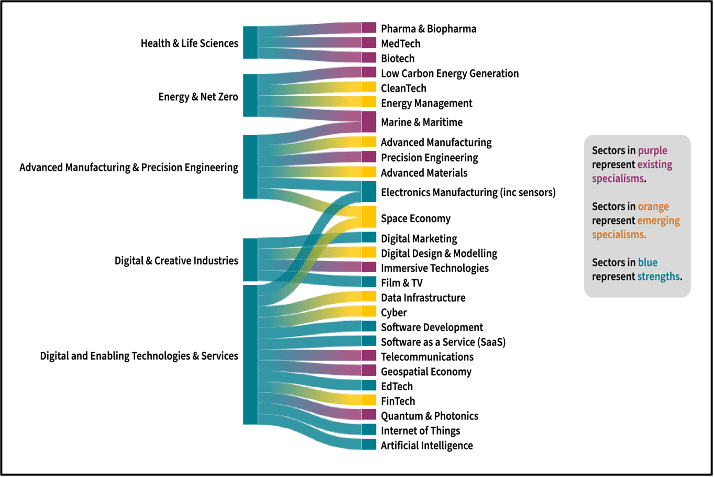
Sources: Intelligence Hub Cluster Baseline
Qualification and Occupation Trends
Glasgow City Region’s workforce has seen an increase in higher qualifications and the increasing proportion of the population employed in professional occupations
The Regional workforce has undergone a transformation over the past two decades. Both the percentage of the population holding higher qualifications and those employed in professional occupations have increased.
These trends suggest that GCR has grown an educated and professionally engaged population.
- These trends have enhanced the Region’s attractiveness to businesses seeking a highly qualified workforce.
But as the proportion of the population with higher qualifications and professional roles increases, demand for such roles might not keep pace with supply. This scenario can lead to underemployment, where highly qualified individuals are compelled to take jobs that do not fully utilise their skills and education, thereby crowding out less qualified workers.
Sources: Annual Population Survey
*Professional Occupations includes Managers, Professional and Associate Professionals
Figure 2: % of professional occupations* in GCR and % of 16-64 with HNC or higher level of qualification
| Professional Occupations | RQF4+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 37.2 | 29.1 | |
| 2005 | 37.4 | 29.4 | |
| 2006 | 38.3 | 31.4 | |
| 2007 | 38.8 | 32.0 | |
| 2008 | 39.2 | 31.6 | |
| 2019 | 44.9 | 43.9 | |
| 2020 | 46.8 | 47.2 | |
| 2021 | 48.0 | 47.7 | |
| 2022 | 47.7 | 51.5 | |
| 2023 | 51.3 | 53.9 | |
| Volume Change Since 2004 | 160,100 | 283,700 |
Graduate Wages tend to be larger than non-graduates, but this effect is weaking in the UK, with premiums paid to those with degrees falling everywhere outside of London
Across the UK the supply of educated labour has increased, but this supply has not always met local demand.
- The Resolution Foundation has shown that weekly pay of graduates aged 21–40 fell by 9% between 2007 and 2021. Over the same period pay for non-graduates of the same age only fell by 2%.
This growth has enabled regions to meet the rising demand for skilled labour in professional, managerial, and technical occupations, particularly in high-growth sectors such as finance, technology, healthcare, and engineering. However, STEM-specific skills remain in relatively scarce supply compared to demand. The wage premium as shown opposite for STEM graduates has either remained stable or increased, compared to others subject areas.
- While there are undersupplies of workers in area like nursing and IT, suggesting mismatch of supply and demand.
Figure 3: University Wage Premia Across UK Regions 1997-2019
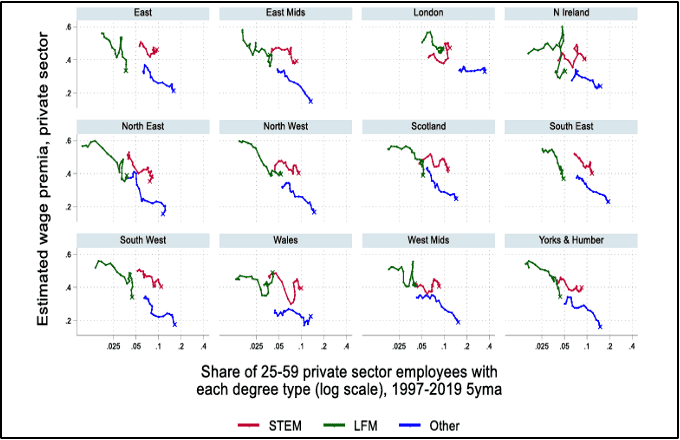
Sources: Economics Observatory, Harvard University, Annual Population Survey, FT
Skill Shortages
Skills shortages and availability of talent continue to act as a major barrier for business expansion in Scotland, according to the Scottish Chamber of Commerce.
The UK has faced prolonged skills shortages exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and Brexit leading to high job vacancy rates and recruitment challenges. Although some of these acute shortages have begun to ease, new challenges and opportunities are emerging, including the impact of AI.
Skills shortages across the UK are having widespread effects on organisations, with both short-term and long-term impacts. In the short term, the most reported consequence is the increased pressure on existing employees, with 68% of respondents indicating that staff workloads have intensified due to these shortages.
- This data suggests that despite rising qualification levels, challenges remain in aligning these skills with labour market demand. Many graduates face skill mismatches and underemployment, where their qualifications do not match job opportunities.
Figure 4: % of total organisations surveyed that are experiencing skills shortages
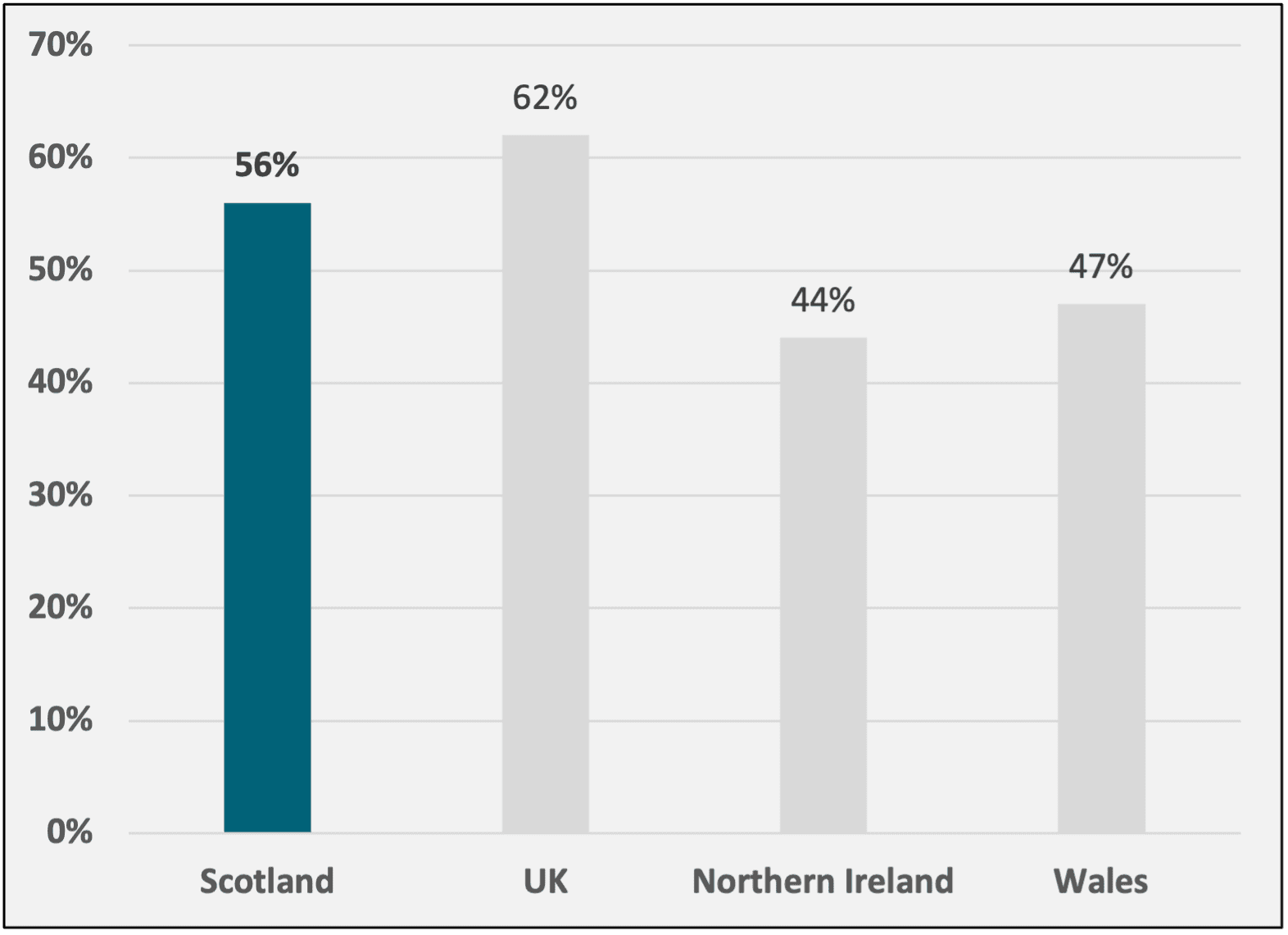
Source: British Chamber of Commerce
Higher and Further Education
The Region’s Strengths
GCR has Higher Education specialisms in subject areas like Computing, Engineering, and Veterinary Sciences.
The Higher Education (HE) sector plays a key role in supporting the regional economy.
- GCR stands out as having the second-highest enrolments among UK core city regions.
The GCR HE sector has clear strengths in STEM related degrees, like Computing and Engineering as shown by its high LQ scoring.
However, more enrolments are retained in areas like Law, Business Management and Education and Teaching.
- Evidence as shown suggests that differences in graduate employment rates and salary prospects, particularly in STEM fields like Computing, Engineering, and Veterinary Sciences, are contributing to this outflow of graduates from the Region.
Sources: HESA, SFC, Harvard University
*HESA Enrolment Data discounts foreign based campuses
Figure 5: Concentration (LQ Scoring) for HE enrolments in each subject area
| Subject Area | LQ | Retention Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| STEM Related | 01 Medicine and dentistry | 1.1 | 37.3% |
| 05 Veterinary sciences | 1.9 | 15.8% | |
| 07 Physical sciences | 1.3 | 28.6% | |
| 09 Mathematical sciences | 1.0 | 34.7% | |
| 10 Engineering and technology | 1.5 | 33.3% | |
| 11 Computing | 1.8 | 40.0% | |
| Social Sciences | 15 Social sciences | 0.7 | 40.3% |
| 16 Law | 0.6 | 47.0% | |
| 17 Business and management | 0.8 | 37.9% | |
| 19 Language and area studies | 1.2 | 32.0% | |
| 20 Historical, philosophical and religious studies | 1.1 | 32.1% | |
| 22 Education and teaching | 1.5 | 48.7% | |
| 23 Combined and general studies | 0.6 | 19.3% |
| Concentrations in enrolments | |
| Above GCR Average Retention Rate |
*Definition of LQ given in Appendix
Economy
Another contributing factor to which HE students are retained within the Region is GCR’s business base.
Most subject areas with strong levels of retention rates within the Region are related to Social Sciences and Management.
The strong specialisation in higher education, particularly in social sciences, law, and education, directly aligns with the region’s employment needs and concentrations in sectors such as public administration, education, and financial and insurance services.
- This means that GCR’s service-based economy has been supported by growing educational attainment and higher retention of Social Science graduates.
| STEM Related | |
| Arts and Culture | |
| Social Sciences and Management Related |
Sources: Oxford Economics, BRES, HESA, Scottish Funding Council
Figure 6: LQ Scoring for HE enrolments in subject areas
| Subject Area | Retention Rate |
|---|---|
| 07 Physical sciences | 28.6% |
| 10 Engineering and technology | 33.3% |
| 15 Social sciences | 40.3% |
| 16 Law | 47.0% |
| 17 Business and management | 37.9% |
| 22 Education and teaching | 48.7% |
Figure 7: LQ Scoring for Employment in broad sectors
| Broad Sector | Employment LQ |
|---|---|
| J : Information and communication | 0.8 |
| M : Professional | 0.8 |
| N : Administrative | 1.2 |
| O : Public administration | 1.6 |
| K : Financial and insurance activities | 0.9 |
| R : Arts, entertainment and recreation | 1.2 |
The Region’s Strengths
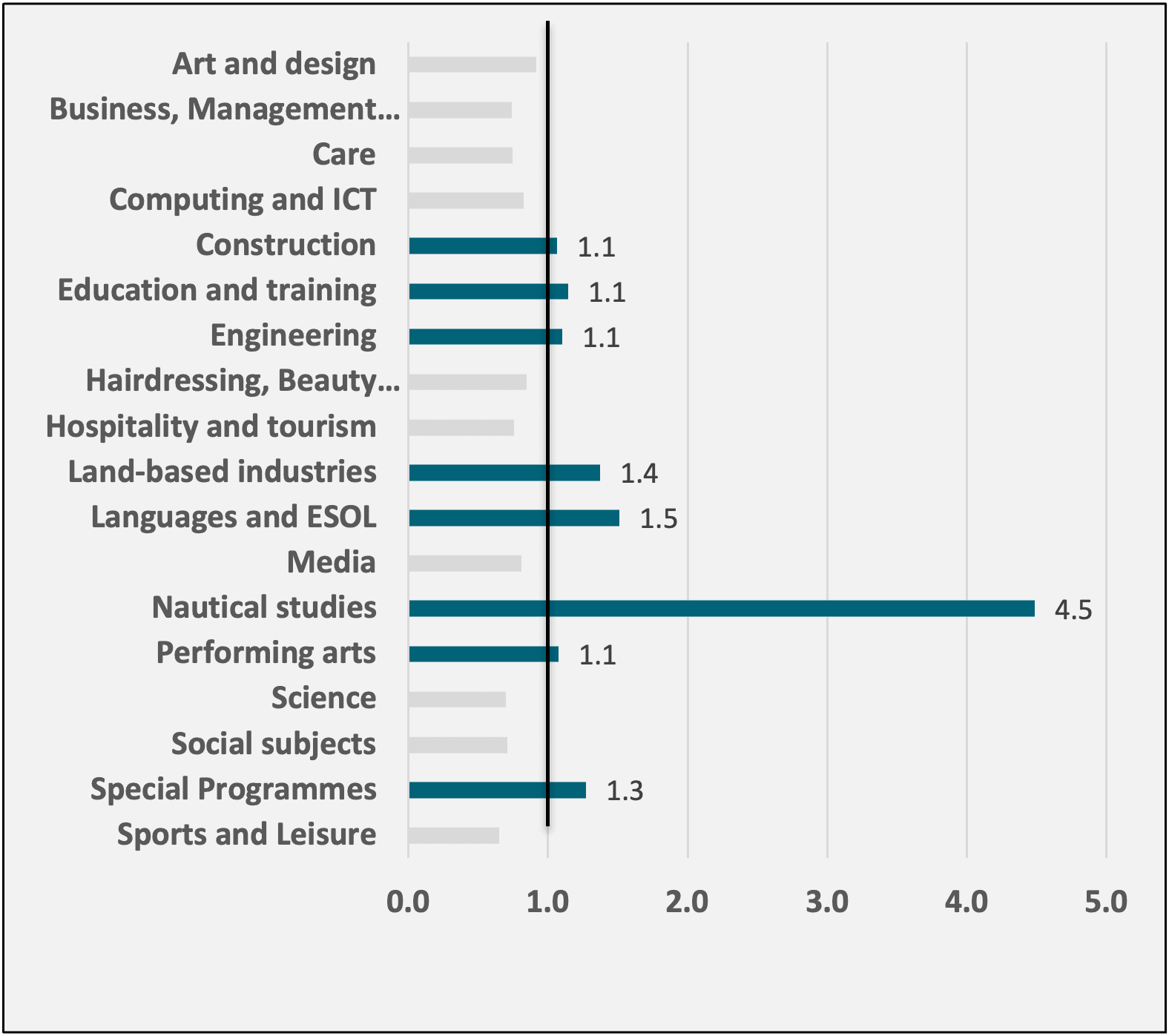
GCR has Further Education specialisms in areas like Nautical Studies, Engineering, Construction and English as a Second Language (ESOL).
Glasgow City Region’s Further Education (FE) sector plays a pivotal role in supporting economy.
FE specialisms such as Nautical Studies, Engineering, Construction, English as a Second Language (ESOL) and Special Programmes like adult vocational courses reflect the Region’s focus on equipping the workforce with practical skills that are highly relevant to the Region’s economic clusters.
For example, Nautical Studies, with a high Location Quotient (LQ) of 4.5, demonstrates a significant concentration and capability in this area, aligning well with the cluster strengths in Marine and Maritime industries.
- Sectors like Digital & Creative Industries, benefit from FE focus on Computing and ICT. The same is for Construction and Engineering, which are crucial to Advanced Manufacturing & Precision Engineering.
Sources: Scottish Funding Council
Figure 8: LQ Scoring for FE graduations in each subject area
Cluster Spotlight
Advanced Manufacturing and Precision Engineering Overview
The Advanced Manufacturing & Precision Engineering cluster has strengths in a range of specialist sectors that have attracted over £244m in investment to GCR since 2008.
Glasgow City Region boasts an advanced manufacturing and engineering ecosystem, housing assets like the Advanced Manufacturing Innovation District Scotland (AMIDS) at its core.
This environment features cutting-edge industry infrastructure and a wide array of research and development centres of excellence. These assets are strengthened by strong collaboration among industry, academia, and the public sector, forming a robust “triple helix” partnership.
- The growth trajectory of the Advanced Manufacturing cluster is shown by the investment in the cluster from 2008 to 2023. The investment trend shows a period of strong capital influx, especially around the late 2010s, indicating targeted efforts to develop the sector and strengthen its competitiveness on a national and global scale.
Figure 9: GCR’s Advanced Manufacturing Ecosystem Scorecard
| Business Count | 157* |
| Location Quotient | 0.67 |
| Estimated GVA/worker | £68,040 |
| Estimated Jobs | 8,500 - 12,000 |
*based on bottom-up review of companies
Sources: DataCity, ONS
Figure 10: Total yearly investment in GCR’s Advanced Manufacturing Cluster
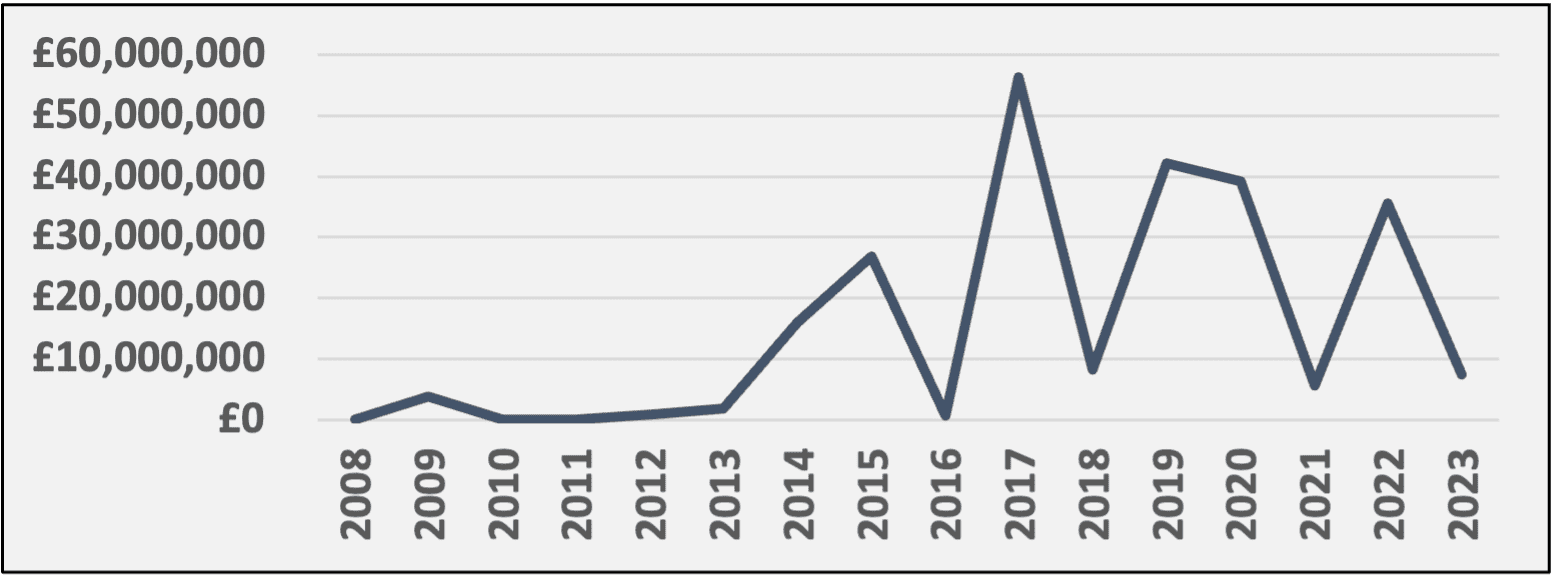
Source: Dealroom
Future Requirements
The wider Manufacturing sector’s occupational requirements are growing and changing amid increased digitisation and automation across the sector.
The forecasts provided by Oxford Economics for SDS presents a clear upward trend in employment across various occupational categories related to manufacturing.
There is significant growth in roles related to Science, Research, Engineering, and Technology, as well as in Associate Science and Engineering.
- In contrast, while Skilled Metal, Electrical, and Electronic Trades, and process, plant and machine operatives are also projected to grow, the pace of this growth is more moderate. This suggests a shift towards more specialised roles within the sector.
- These trends reflect the transformation of the manufacturing industry, where automation, digitalisation, and precision engineering are becoming increasingly important.
This further highlights the need for a flexible and agile skills delivery system for GCR.
Figure 11: Real & Forecast Manufacturing related occupations in GCR
| Relevant Occupations | 2023 | 2023-26 | 2026-33 | 10 Year % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Science, research, engineering and technology | 72,100 | 82,400 | 105,500 | 46.3% |
| Associate Science, engineering and technology | 25,100 | 31,400 | 45,800 | 82.5% |
| Skilled metal, electrical and electronic trades | 37,300 | 39,200 | 43,000 | 15.3% |
| Process, plant and machines operatives | 10,800 | 11,100 | 11,300 | 4.6% |
| Total Manufacturing Related | 145,300 | 164,100 | 205,600 | 41.5% |
Source: Annual Population Survey, SDS Regional Skill Assessment
Policy Response
Glasgow City Region is developing several evidence backed programmes aimed at addressing skills issues to Regional Economic Objectives.
Future Skills Programme
The Future Skills Programme aims for skills devolution, building a flexible system that adapts to changing demands.
Flexible to Needs: Collaboration with employers and educational institutions will be central to better aligning skills provision with market requirements, ensuring that the GCR workforce is equipped to support economic growth and innovation. By enhancing employer engagement, expanding regional partnerships, and streamlining funding, the policies aim to mitigate skills shortages.
Current Programmes: The Multiply Programme falls under regional skills policy, which is focused on improving numeracy skills among adults, aiming to boost employment prospects and support lifelong learning, thereby addressing skill gaps and enhancing economic participation across Glasgow City Region.
Innovation Action Plan
The Glasgow City Region Innovation Action Plan outlines a commitment to enhancing skills as a core area of innovation.
Skills Pipeline: The plan emphasises building a robust, integrated pipeline of talent to support the region’s innovation economy. This involves enhancing the skills base to ensure a steady supply of skilled workers who can meet the demands of innovation-driven businesses.
Partnership Working: The action plan aims to leverage partnerships with universities and colleges to boost the capacity for innovation in the Scottish economy.
Entrepreneurial and Innovation Skills development: Various initiatives are to be trialled because of the Innovation Action Plan. Two key Innovation Districts within the City, GCID and GRID are delivering various skills development programmes to promote innovation within businesses and individuals.
Appendix 1
Economic and Labour Market Headline Data
ONS Labour Market estimates from May to July 2024
| Unemployment (%) | Unemployment (ppts) Quarter Change | Employment (%) | Employment (ppts) Quarter Change | Economic Inactivity (%) | Economic Inactivity (ppts) Quarter Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scotland | 3.9 | -0.9 | 73.7 | 0.8 | 23.2 | -0.1 |
| UK | 4.0 | -0.4 | 75.0 | 0.6 | 21.8 | -0.3 |
Latest Headline National Economic Indicators
| Monthly GDP % Change | Inflation | Inflation (ppts) Monthly Change | Annual Average Wages Growth | Wages (ppts) Previous Period Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK | 0.2% | 1.7% | -0.5 | 4.9% | -0.2 |
Sources: ONS GDP, ONS Pay, ONS Inflation
Glossary
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The total monetary value of final good and services produced in a country in a given time period.
Consumer Price Index (CPI): Is a weighted-average of a basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI tracks changes in prices overtime.
Unemployment rate: Unemployed people are out of work but actively looking for a job and available to start work in the next two weeks. It is measured as the number of unemployed people divided by the number of economically active population (those in employment and those unemployed).
Economic Inactivity: People who are not in the workforce are classified as economically inactive and have not been seeking work for the last four weeks and cannot start in the next two weeks.
Location Quotient (LQ): Location Quotient (LQ) is a measure to assess the concentration of a particular industry, occupation, or demographic group within a region compared to a larger reference area, such as a country. It is calculated by taking the ratio of an industry’s share of total regional employment/gva/student numbers to that industry’s share. An LQ greater than 1 indicates that the region has a higher concentration of that industry compared to the national average, suggesting potential specialisation or competitive advantage in that specific area. Conversely, an LQ less than 1 indicates a lower concentration than the national average.
Further Information
For queries and further information, please contact Will Harkiss:







